Network topologies define how devices connect in a network. This guide explains different types, their structures, and how they function.
Imagine you’re setting up a town where all the houses need to be connected with roads. The way you design those roads—whether they all lead to a central square, form a circular route, or crisscross everywhere—determines how easily people can travel and communicate.
Network topology works the same way, but instead of roads and houses, we’re talking about cables and devices in a computer network.
What is Network Topology?
Network topology is how computers and devices (like routers, switches, and servers) are connected in a network. It determines how data travels between them and affects the speed, reliability, and efficiency of communication.
Physical vs. Logical Topology
- Physical Topology: This is how devices are physically arranged and connected using cables or wireless signals.
- Logical Topology: This describes how data actually moves through the network, regardless of the physical layout.
Now, let’s explore different types of network topology with simple explanations and relatable examples.
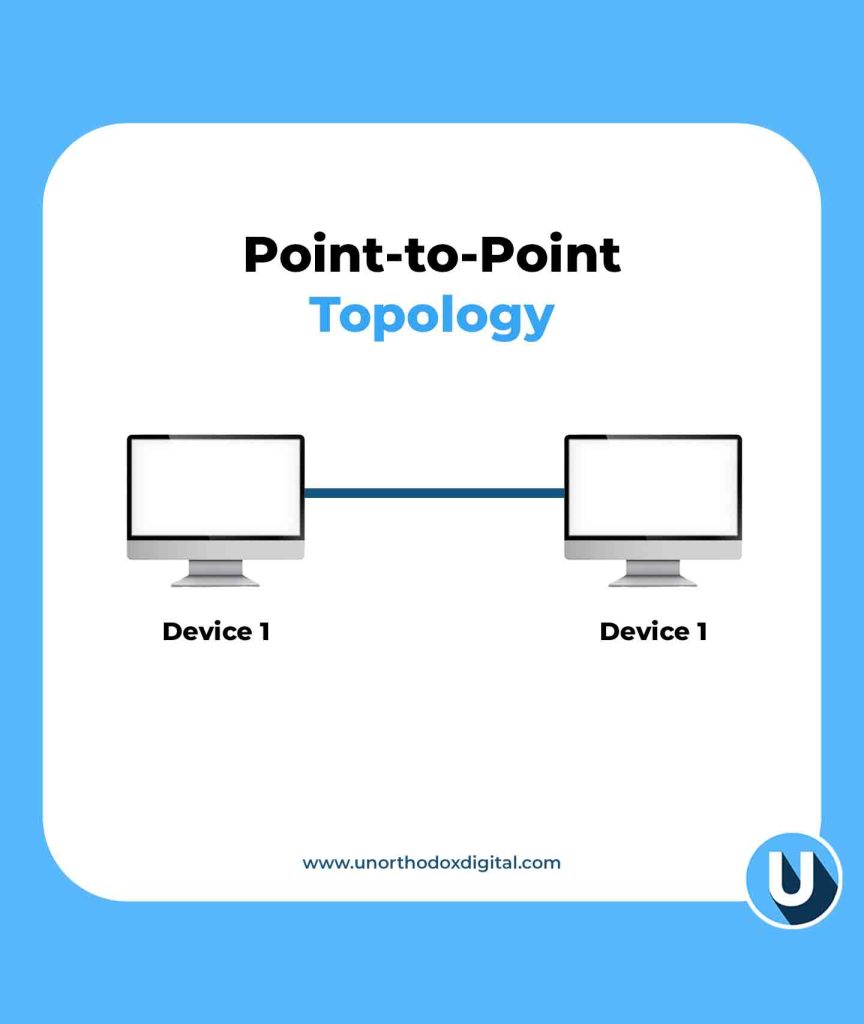
1. Point-to-Point Topology
The Point-to-Point Topology is the simplest form of a network—just two devices directly connected to each other.
Example: Imagine two people using walkie-talkies. One talks, the other listens, and they take turns. That’s a point-to-point connection.
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
| Simple setup | Limited to just two devices |
| Fast communication | No flexibility to add more devices |
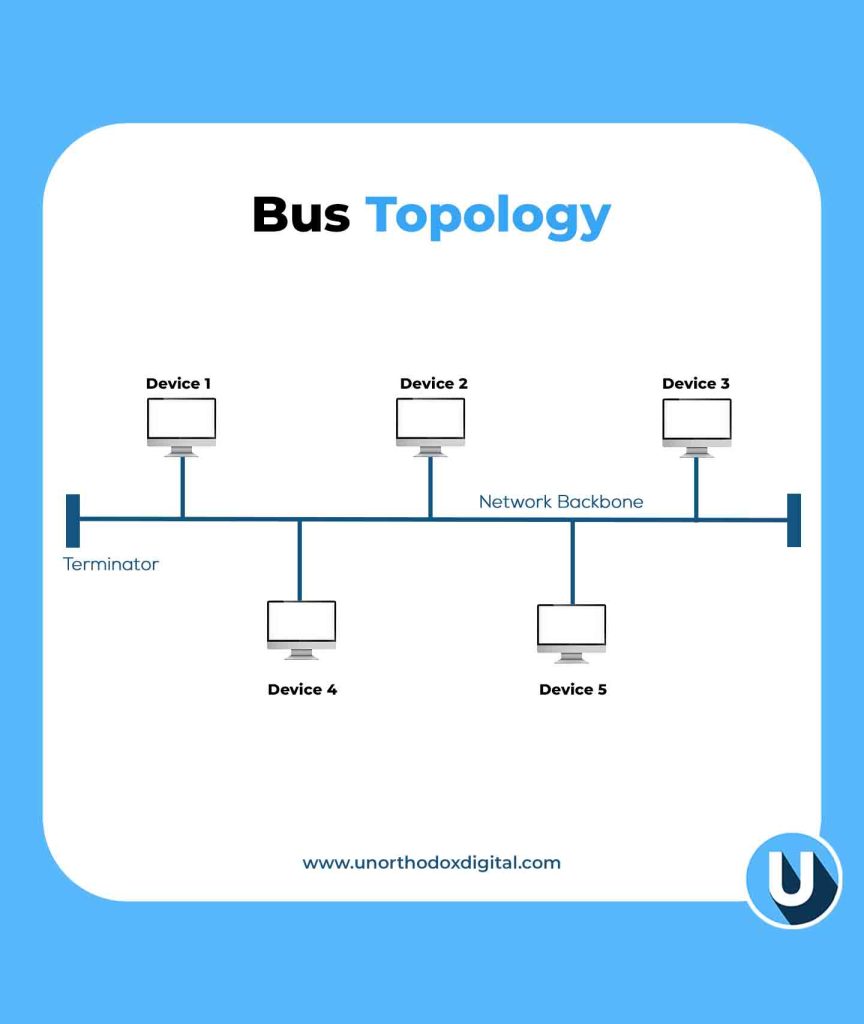
2. Bus Topology
In the Bus Topology, all devices are connected to a single main cable (called a backbone), and data travels in both directions.
Example: Think of a public bus route. If one bus stop (device) has a problem, other stops might be affected.
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
| Cost-effective (less cable needed) | If the main cable fails, the whole network goes down |
| Easy to expand | Performance slows down with more devices |
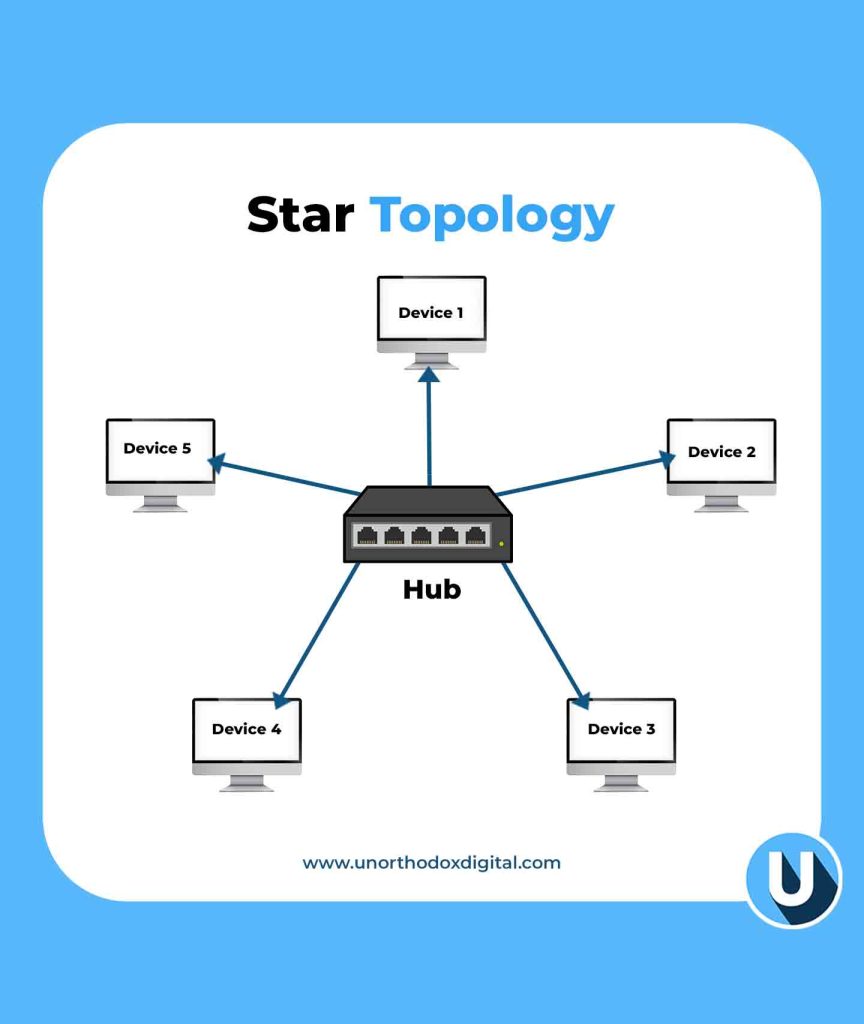
3. Star Topology
In the Star Topology, all devices connect to a central hub or switch, which acts like a traffic controller for data.
Example: Imagine an airport where all flights must go through a central control tower. If the tower is down, flights can’t take off.
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
| Easy to manage and troubleshoot | If the central hub fails, the whole network stops working |
| Adding or removing devices is simple | More cabling required |
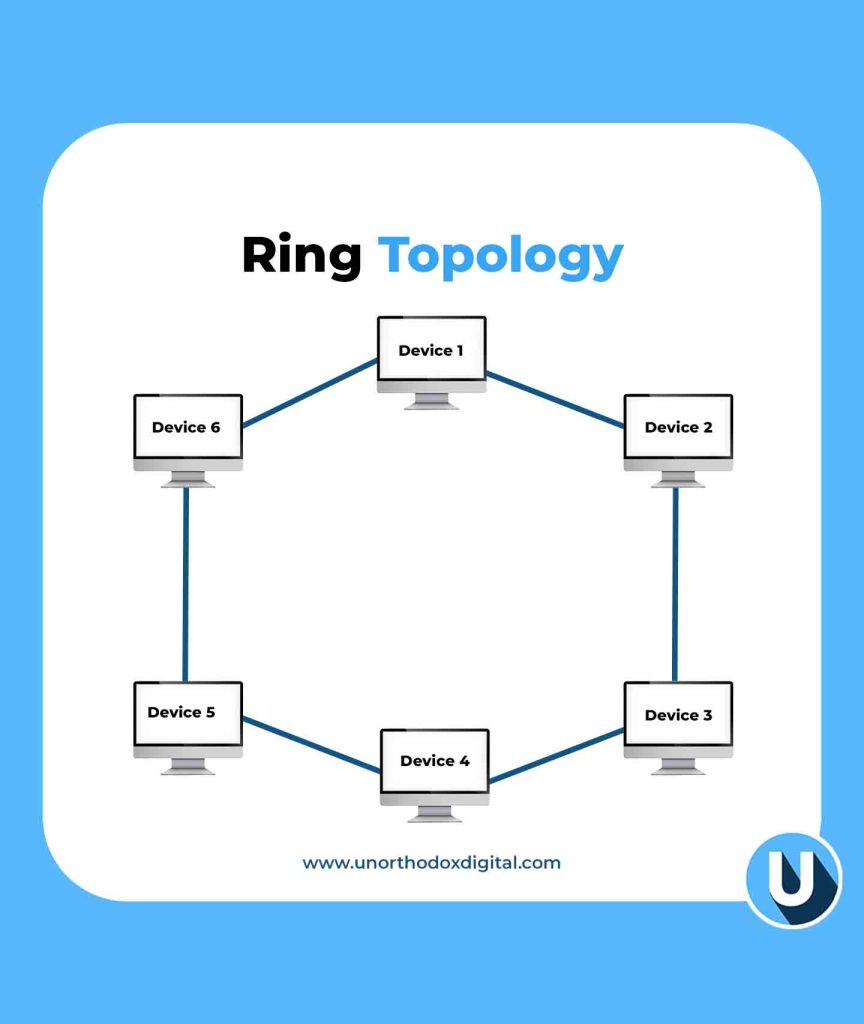
4. Ring Topology
This setup, known as a Ring Topology, connects each device to two others, forming a circular data path. Data travels in one direction (or both in a dual-ring setup), ensuring a structured and efficient flow.
Example: Think of a relay race where a baton (data) is passed from runner to runner (device) until it reaches the destination.
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
| No data collisions | If one device fails, the entire network can break |
| Predictable data flow | Adding new devices can disrupt the network |
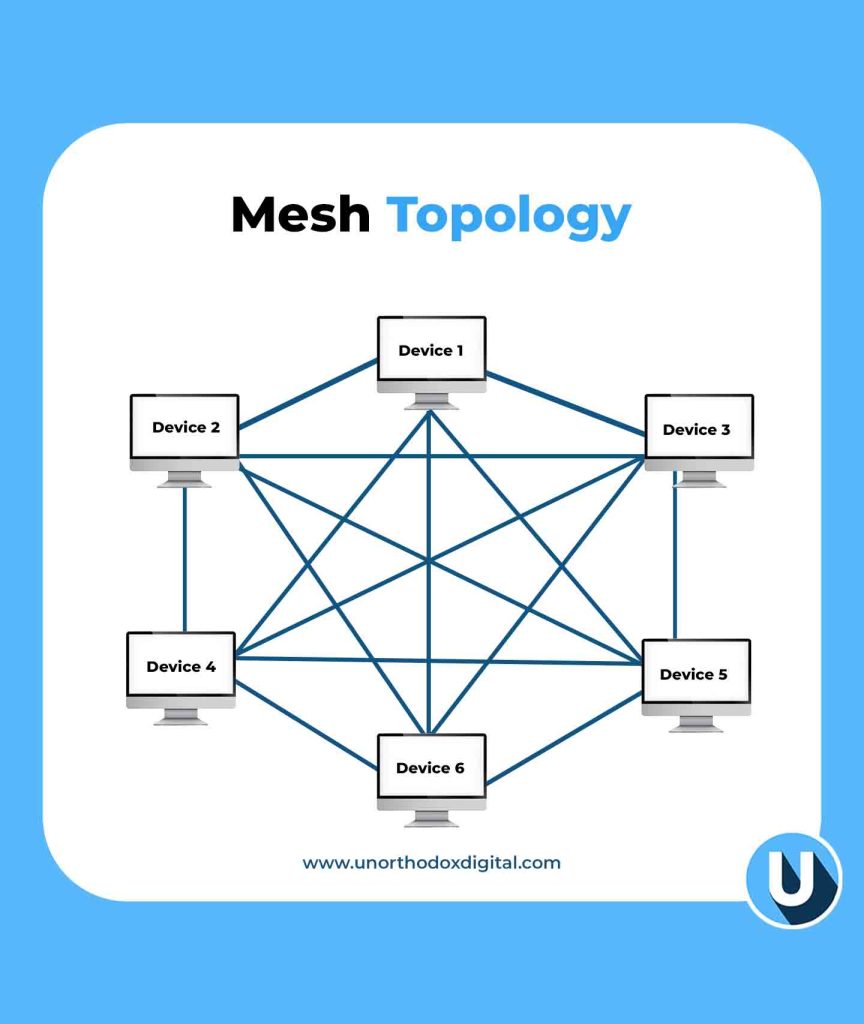
5. Mesh Topology
In the Mesh Topology, every device is connected to every other device, creating multiple paths for data.
Example: Think of a spider web. If one strand breaks, there are still plenty of other ways for the spider to move around.
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
| Very reliable (data can take multiple routes) | Expensive and complex to set up |
| If one link fails, data can still reach its destination | Requires a lot of cabling |
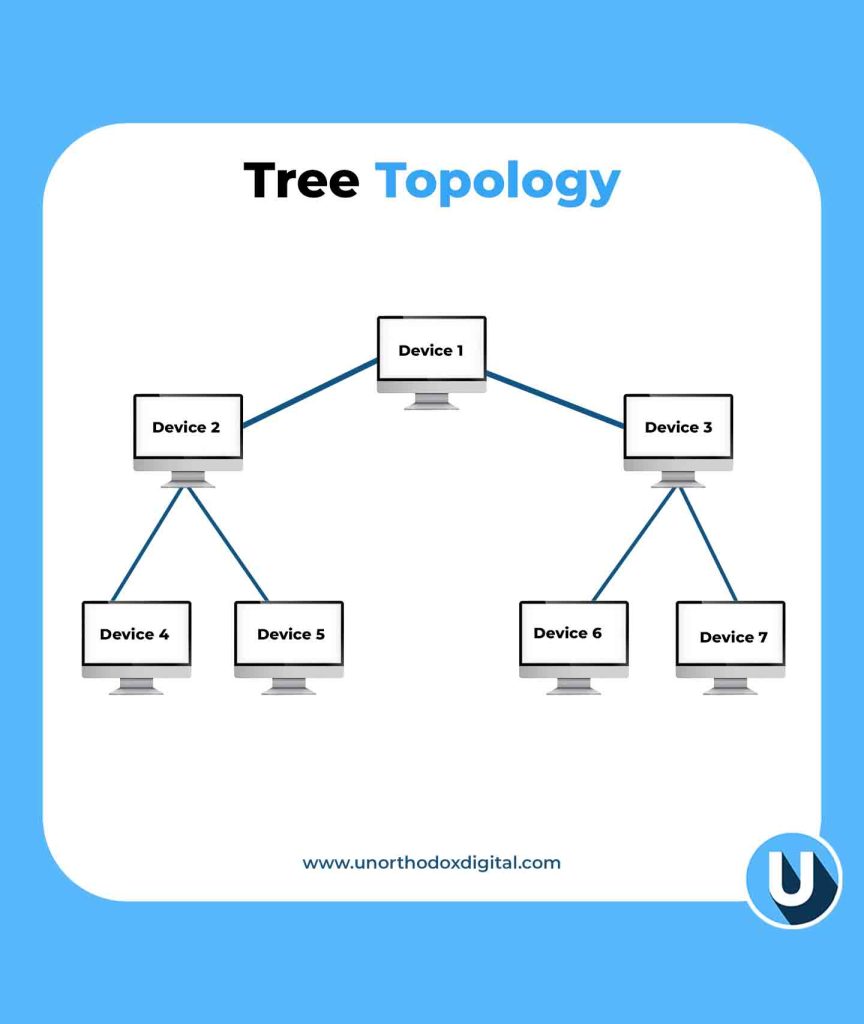
6. Tree Topology
The Tree Topology is a mix of star and bus topologies, with multiple branches stemming from a central hub.
Example: Think of a big family tree. The oldest generation (main hub) connects to multiple generations (sub-hubs and devices).
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
| Easy to expand and manage | If the main hub fails, the entire network can go down |
| Well-structured hierarchy | Requires more cabling and configuration |
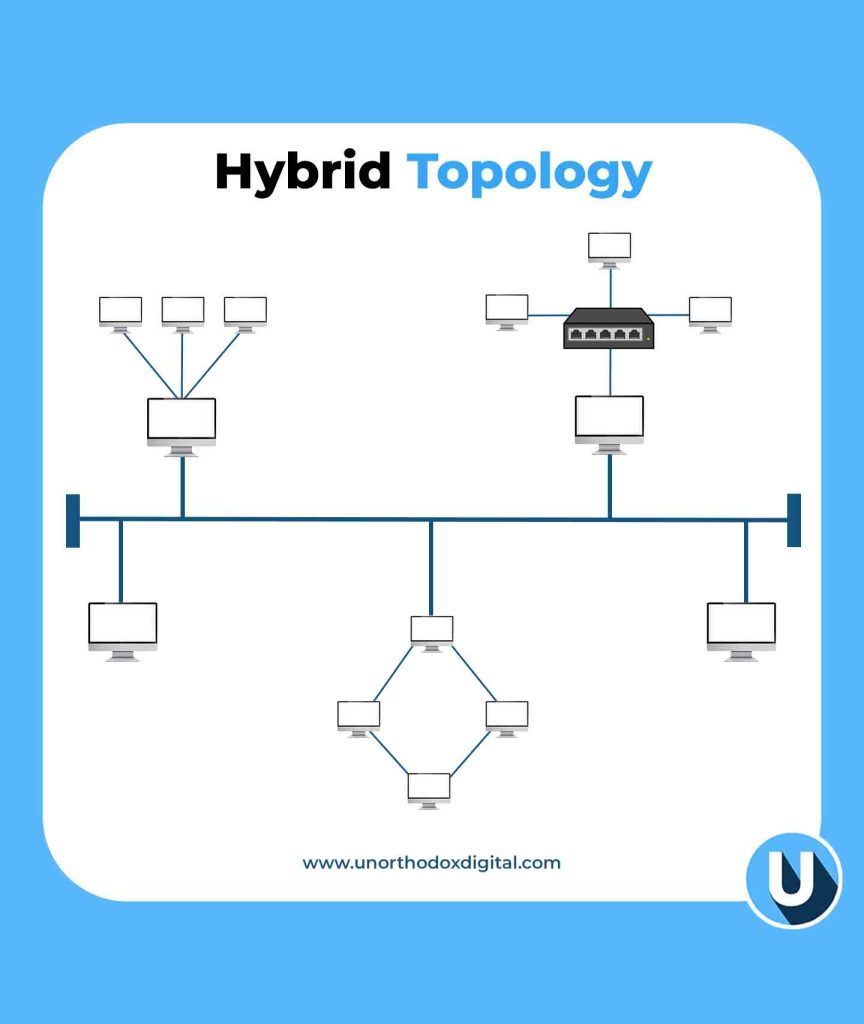
7. Hybrid Topology
The Hybrid Topology is a combination of two or more topologies, depending on the needs of the network.
Example: A university might have a star topology in classrooms, a bus topology in dormitories, and a mesh topology for research labs.
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
| Highly flexible and scalable | Complex to design and maintain |
| Best for large organizations | Expensive setup |
Why Does Network Topology Matter?
Choosing the right network topology is important because it affects:
- Performance: A good layout ensures fast and efficient communication.
- Reliability: Some topologies provide backup routes if a connection fails.
- Cost: More complex topologies need more cables and hardware.
- Scalability: Some layouts make it easier to add new devices without disrupting the network.
Network topology might sound technical, but at its core, it’s just about how devices talk to each other. Whether it’s a simple point-to-point connection or a complex hybrid setup, the right choice depends on what you need. Just like choosing the best road layout for a town, picking the right network topology ensures smooth communication and efficiency.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Is it possible to use multiple network topologies together?
Yes, a network can combine different topologies in a hybrid setup. This approach enhances flexibility, performance, and reliability by leveraging the strengths of multiple structures.
What factors should be considered when selecting a network topology?
The choice of topology depends on factors such as network size, budget, performance requirements, scalability, and reliability. Evaluating these elements helps in selecting the most efficient structure.
Which network topology is the most cost-effective and easiest to implement?
Bus topology is the simplest and most affordable to set up, as it connects all devices using a single main cable. However, it is better suited for smaller networks due to its limitations.
Why do large networks often use hybrid topology?
Hybrid topology is widely used in large networks because it integrates multiple topologies, allowing for greater flexibility and optimization based on specific networking requirements.
What is the most suitable topology for large-scale networks?
For large-scale networks, mesh and tree topologies are commonly used. Mesh topology ensures high reliability through redundant connections, while tree topology supports scalability and efficient data management.
Subscribe to our Newsletter
Stay updated with the latest trends in African technology!