Imagine you run a bakery that gets hundreds of orders every day. Instead of baking each cake one at a time, you group similar orders together—chocolate cakes in one batch, vanilla cakes in another. This way, you save time and effort by completing similar tasks all at once. Computers work in a similar way when using a batch processing operating system.
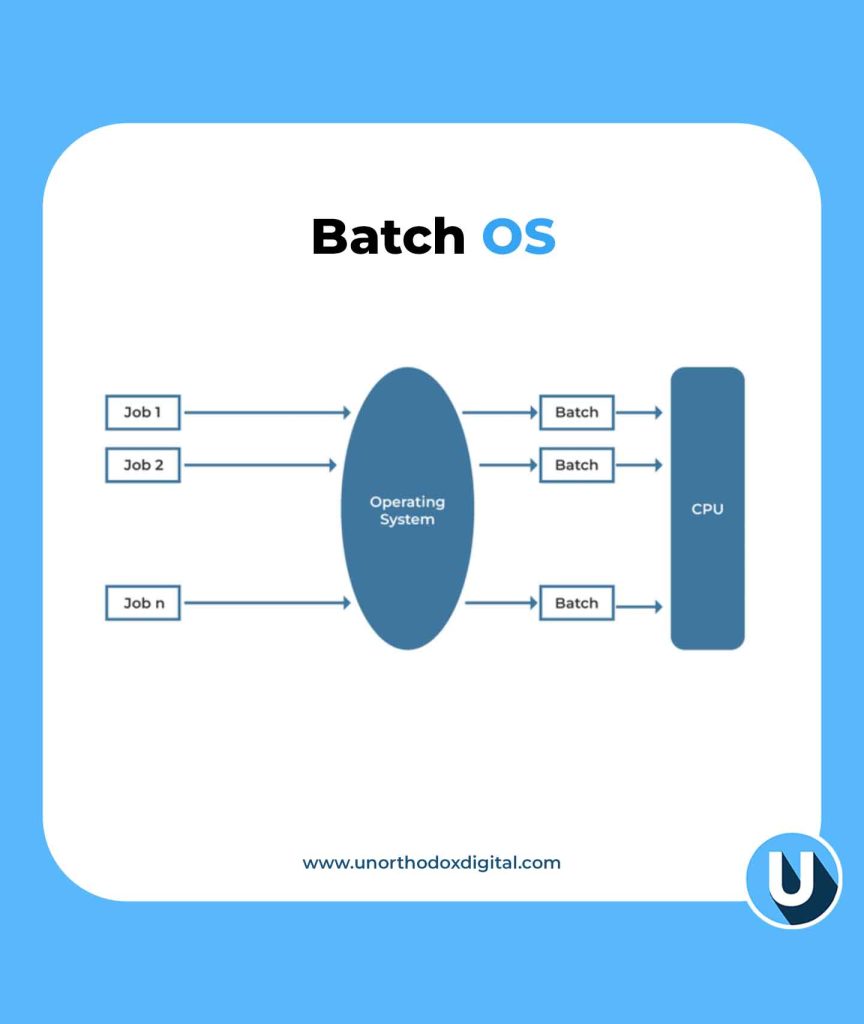
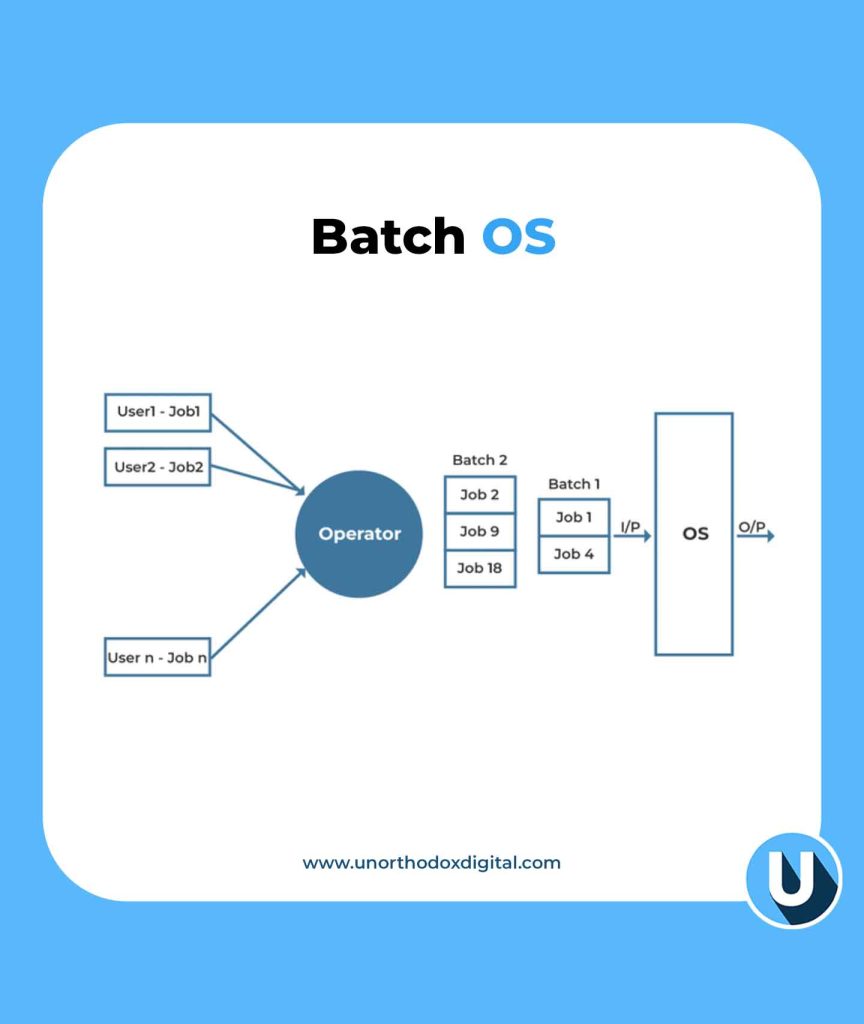
A batch processing operating system (Batch OS) is a type of operating system that processes jobs in groups or batches without direct user interaction. This method was commonly used in early computer systems and is still useful today for handling large amounts of data efficiently.
How Batch Processing Works
Batch processing follows a simple cycle:
- Users submit jobs – These jobs can be anything from processing payrolls to sorting large amounts of data.
- The system groups jobs – Jobs with similar requirements (like needing the same type of processing or input) are placed together in batches.
- Jobs are executed automatically – Once a batch is ready, the system runs it without requiring manual intervention.
- Results are delivered – The system processes all jobs in the batch and provides the output once the batch is completed.
To better understand, think of it as a washing machine. Instead of washing each piece of clothing separately, you wait until you have a full load, then wash everything at once. The machine (like the computer) does all the work for you without needing your attention.
Features of Batch Processing Operating Systems
Batch OS comes with unique features that make it effective for processing large amounts of data. Here are some of its main characteristics:
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Automatic Job Execution | Jobs are executed in batches without manual input once submitted. |
| Efficient Resource Use | The system maximizes the use of resources by grouping similar jobs together. |
| Job Scheduling | The system schedules jobs based on priority and available resources. |
| Error Handling | Since jobs are processed without user interaction, error logs help in debugging later. |
| High Throughput | Processes multiple jobs quickly, increasing efficiency. |
| Minimal User Interaction | Once jobs are submitted, users don’t need to stay involved. |
Real-World Examples of Batch Processing
Batch processing is used in various industries for handling repetitive tasks efficiently. Some examples include:
| Industry | Example of Batch Processing |
| Banking | Processing customer transactions at the end of the day. |
| Payroll Systems | Companies process employee salaries in batches at the end of each month. |
| Government Agencies | Census data is processed in batches after collection. |
| Weather Forecasting | Data is collected and processed in batches to generate forecasts. |
| Airline Reservations | Large volumes of ticket bookings are handled in batches. |
Advantages of Batch Processing Operating Systems
Batch processing offers multiple benefits, making it ideal for handling large-scale tasks. Here’s why it’s widely used:
- Efficiency – It processes multiple jobs together, reducing processing time and improving system performance.
- Cost-Effective – Since jobs are handled in bulk, companies save money on operational costs.
- Error Reduction – By automating tasks, the chances of human errors decrease.
- Better Resource Utilization – Resources like CPU and memory are used efficiently, preventing wastage.
- No User Dependency – Once submitted, jobs run without requiring continuous user input.
- Handles Large Volumes of Data – Ideal for processing massive datasets, such as payroll or government records.
Disadvantages of Batch Processing Operating Systems
Despite its benefits, batch processing has some limitations:
- Delayed Output – Since jobs are processed in batches, results aren’t immediate.
- Difficult Debugging – If an error occurs, finding the exact job that caused the issue can be time-consuming.
- Resource Locking – While processing a batch, the system might be unavailable for other tasks.
- Not Ideal for Real-Time Processing – If a job requires immediate feedback, batch processing isn’t the best option.
Types of Batch Processing Systems
There are different types of batch processing systems, each suited for specific use cases:
| Type | Description |
| Simple Batch System | Jobs are collected and processed sequentially without prioritization. |
| Scheduled Batch System | Jobs are scheduled based on priority and system availability. |
| Concurrent Batch System | Multiple batches are processed simultaneously to improve efficiency. |
| Real-Time Batch System | Processes jobs as soon as a batch is formed, reducing waiting time. |
Examples of Batch Processing Operating Systems
Some well-known batch processing operating systems include:
| Operating System | Organization |
| IBM’s z/OS | IBM |
| Unisys MCP | Unisys |
| Burroughs MCP/BCS | Burroughs Corporation |
| OS/1100 | UNIVAC |
| GCOS | Honeywell |
| MVS | IBM |
Batch Processing vs. Real-Time Processing
Batch processing is often compared to real-time processing. Let’s look at how they differ:
| Feature | Batch Processing | Real-Time Processing |
| Execution Mode | Jobs processed in bulk | Jobs processed instantly |
| User Interaction | No immediate interaction | Requires user input and quick response |
| Use Case | Payroll, census, large-scale data processing | ATM transactions, airline ticket booking, live monitoring |
| Error Handling | Errors identified after processing | Errors handled immediately |
| Response Time | Delayed output | Immediate output |
Batch processing operating systems play a crucial role in handling large amounts of data efficiently. By grouping similar jobs together, these systems optimize resources, reduce errors, and save time. While they aren’t ideal for tasks that require immediate responses, they are perfect for scenarios where high-volume processing is needed. From banking and payroll to weather forecasting and airline reservations, batch processing remains a key component of computing.
Understanding batch processing helps in recognizing why some tasks happen in the background while you wait for results. The next time your bank updates your transaction history overnight, you’ll know it’s thanks to batch processing!